Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM) FAQ’s
Q1) What are the types of VSAM datasets ?
A1) Entry sequenced datasets (ESDS), key sequenced datasets (KSDS) and relative record dataset (RRDS).
Q2) How are records stored in an ESDS, entry sequenced dataset ?
A5) They are stored without respect to the contents of the records and in the order in which they are included in the file.
Q3) What is a CI, control interval ?
A3) A control interval is the unit of information that VSAM transfers between virtual and auxiliary storage.
Q4) What are the distinctive features of a ksds, key sequenced dataset ?
A4) The index and the distributed free space.
Q5) What is a CA, control area ?
A5) A group of control intervals makes up a control area.
Q6) What is a sequence set ?
A6) This is the part of the index that points to the CA and CI of the record being accessed.
Q7) What is the index set ?
A7) This is the other part of the index. It has multiple levels with pointers that ultimately reach to the sequence set.
Q8) What is a cluster ?
A8) A cluster is the combination of the index, sequence set and data portions of the dataset. The operating system gives program access to the cluster, ie. to all parts of the dataset simultaneously.
Q9) What is the catalog ?A9) The catalog contains the names of all datasets, VSAM and non-VSAM. It is used to access these datasets.
Q10) What is an alternate index ?A10) An AIX is a file that allows access to a VSAM dataset by a key other than the primary one.
Q11) What is a path ?A11) A path is a file that allows you to access a file by alternate index - the path provides an association between the AIX and the base cluster.
Q12) What is the upgrade set ?A12) The upgrade set is the list of all AIXes that VSAM must maintain for a specific base cluster, so that when data in the base cluster is updated, the AIX files are also updated.
Q13) What is free space ?A13) Free space is reserved within the data component of a KSDS to accommodate inserting new records.
Q14) What is a VSAM split ?A14) If there isn't enough space in the control interval VSAM performs a control interval split by moving some records to the free control intervals. If there isn't a free control interval VSAM performs a control area split by allocating a new control area and moving half of the control intervals to it.
Q15) What is the base cluster ?A15) The base cluster consists of the data component and the index component for the primary index of a KSDS.
Q16) Do primary key values have to be unique ? Do alternate key values have to be unique ?A16) Primary key values must be unique; alternate key values need not be.
Q17) In the COBOL SELECT statement what is the ORGANIZATION for a KSDS ?A17) The ORGANIZATION is INDEXED.
Q18) In the COBOL SELECT statement for a KSDS what are the three possibilities for ACCESS ?A18) ACCESS can be SEQUENTIAL, RANDOM or DYNAMIC.
Q19) What is the COBOL RECORD KEY clause ?A19) The RECORD KEY in the SELECT clause identifies the files primary key as it will be known to the program.
Q20) What is the purpose of the FILE STATUS clause in the SELECT statement ?A20) The FILE STATUS field identifies the field that VSAM uses to provide information about each I/O operation for the file.
Q21) If you wish to use the REWRITE command haw must the VSAM file be opened ?A21) It must be opened as I/O.
Q22) Explain the meaning and syntax for the START command.
A22) The START command is used read other than the next VSAM record. A value must be moved into the RECORD KEY. The KEY clause is optional, but it can be used to specify a relational (equal, less than, etc.) operator.
Q23) What is the meaning of dynamic processing ?A23) It's rarely used. It means one program uses both sequential and random processing for a VSAM KSDS file.
Q24) Name some common VSAM error conditions and codes.
A24) They are end of file (10), duplicate key (22), record not found (23), VSAM logic error (90), open problem (92) and space problem (93).
Q25) What is the VSAM-code field ?A25) It is a COBOL II enhancement to VSAM batch processing expanding the FILE STATUS field. It is defined in WORKING-STORAGE as a six byte group item with three two byte elements, the normal return code, the function code and the feedback code.
Q26) What is a VSAM slot ?A26) A relative record dataset (RRDS) consists of a specified number of areas called slots. Each slot is identified by a relative record number (RRN) which indicates its relative position in the file.
Q27) What is the utility program closely associated with VSAM ?A27) IDCAMS, the access method services utility.
Q28) There are at least seven IDCAMS commands; name and explain each of them ?.
A28) ALTER modifies information for a catalog, alternate index, cluster or path. BLDINDEX builds the alternate index, of course. DEFINE is used for ALTERNATEINDEX, CLUSTER or PATH. DELETE removes the catalog entry for a catalog, cluster, alternate index or path. LISTCAT lists information about the dataset. PRINT prints the dataset contents. REPRO copies records from one file to another.
Q29) What are the three levels of definition for the VSAM DEFINE ?A29) They are DEFINE CLUSTER, DATA and INDEX.
Q30) What is the significance of the SHAREOPTIONS parameter ?A30) It specifies how the file may be shared between jobs and between batch and CICS environments.
Q31) What is the meaning of the DEFINE MODEL parameter ?A31) It specifies whether Daniela Pestova or Yamila - oops! Wrong models! The MODEL parameter allows you to model your cluster by modeling it after an existing cluster.
Q32) What is File Status in VSAM ?A32) The FILE STATUS clause of the FILE-CONTROL paragraph allows for each file to be associated with a file status key (i.e., the 2-character data item specified in the FILE STATUS clause). If the FILE STATUS clause is specified for a given file, a value indicating the status of each I/O operation against that file is placed in the associated file status key. This value is stored in the file status key as soon as the I/O operation is completed (and before execution of any EXCEPTION/ERROR declarative or INVALIDKEY/AT END phrase associatedwith the I/O request).
Note: This element may behave differently when the CMPR2 compiler option is used. The file status key is divided
into two status keys: the first character is known as file status key 1; the second character is file status key 2.
Q33) What's a LDS (Linear Data Set) and what's it used for ?A33) LDS is a VSAM dataset in name only. It has unstructured 4k (4096 bytes) fixed size CI’s which do not contain control fields and therefore from VSAM's standpoint they do not contain any logical records. There is no free space, and no access from Cobol. Can be accessed by DB2 and IMS fast path datasets. LDS is essentially a table of data maintained on disk. The 'table entries' must be created via a user program and can only be logically accessed via a user program. When passed, the entire LDS must be mapped into storage, and then data is accessed via base and displacement type processing.
Q34) What is IDCAMS ?A34) IDCAMS is the Access Method Services program. You run the IDCAMS program and supply AMS commands thru SYSIN. (examples of AMS commands are DELETE, DEFINE, REPRO etc..).
Q35) Can AMS commands be run from the TSO prompt ?A35) Yes
Q36) Syntax of AMS modal commands ?A36) Note: these can be used only under IDCAMS and not from the TSO prompt.
IF LASTCC(or MAXCC) >(or <,= etc..) value -
THEN -
DO -
command set (such as DELETE, DEFINE etc..)
ELSE -
DO -
command set
LASTCC - Condition code from the last function (such as delete) executed
MAXCC - Max condition code that was returned by any of the prev functions
SET is also a valid AMS command. SET LASTCC (or MAXCC) = value
The maximum condition code is 16. A cond code of 4 indicates a warning. A cond code of 8 is usually encountered on a DELETE of a dataset that is not present.
Q37) Under IDCAMS , multiple functions can be executed, each of which returns a cond code. What will be the condition code returned to the operating system ?A37) The maximum condition code generated is returned as the condition code of the IDCAMS step.
Q38) What is Control Interval, Control Area ?A38) Control Interval is analogous to a physical block for QSAM files. It is the unit of I/O. Must be between 512 bytes to 32 k. Usually either 2K or 4K. A larger control interval increases performance for sequential processing while the reverse is true for random access. Under CICS when a record is locked, the entire CI gets locked.
Control Area is a group of control intervals. CA is used during allocation. CA size is calculated based on the
allocation type (cyl, tracks or records) and can be max of 1 cylinder
Q39) What is FREESPACE ?A39) Coded in the DEFINE as FREESPACE(ci ca) where ci is the percentage of each control interval to be left free for insertions, ca is the percentage of control intervals in each control area to be left empty.
Q40) How do you decide on optimum values for CI, FREESPACE etc... ?A40) CI size should be based on record length, type of processing. Usually CI is 4K. If record length is larger(>1K), chose 6K or 8K. FREESPACE should be large if more number of insertions are envisaged. Usual values are (20 20) when heavy updates are expected. CI size can be calculated.
Q41) Would you specify FREESPACE for an ESDS ?A41) No. Because you cannot insert records in an ESDS, also when you rewrite a record, it must be of the same length. Thus putting any value for freespace does not make any sense.
Q42) What is SHAREOPTS ?A42) SHAREOPTS is a parameter in the DEFINE and specifies how an object can be shared among users. It is coded as SHAREOPTS(a b), where a is the cross region share option ie how two or more jobs on a single system can share the file, while b is the cross system share option ie how two or more jobs on different MVS’s can share the file. Usual value is (2 3).
Q43) What is the meaning of each of the values in SHAREOPTS(2 3) ?A43) Value of 2 for cross region means that the file can be processed simultaneously by multiple users provided only one of them is an updater. Value of 3 for cross system means that any number of jobs can process the file for input or output (VSAM does nothing to ensure integrity).
Q44) How do you define a KSDS ?A44) DEFINE CLUSTER(cluster name) with the INDEXED parameter. Also specify the ds name for the DATA component & the ds INDEX component. Other important parms are RECORDSIZE, KEYS, SHAREOPTIONS.
Q45) How do you define an ALTINDX ? How do you use ALTINDXs in batch, CICS pgm’s ?A45) DEFINE ALTERNATEINDEX. Important paramters are RELATE where you specify the base cluster name, KEYS, RECORDSIZE,SHAREOPTIONS,UNIQUEKEY(or NONUNIQUEKEY), DATA(ds name for the data component), INDEX(ds name for the index component). Then DEFINE PATH. Important paramters are NAME (ds name for the path), PATHENTRY (ds name of the alternate index name), UPDATE(or NOUPDATE) which specifies whether an alt index is updated when a update to the base cluster takes place. Then BLDINDEX. Parameters are INDATASET(ds name of base cluster), OUTDATASET(ds name of AIX).
Q46) Using Alternate Indexes in Batch pgms:
A46) In the JCL, you must have DD stmts for the cluster and for the path(s). In the COBOL Program, SELECT .. ASSIGN TO ddname for base cluster RECORD KEY IS... ALTERNATE RECORD KEY IS..
Q47) Using Alternate Indexes in CICS pgms:
A47) FCT entries must be created for both base cluster & the path. To read using the alternate index, use the dd name of the path in CICS file control commands.
Q48) What happens when you open an empty VSAM file in a COBOL program for input ?A48) A VSAM file that has never contained a record is treated as unavailable. Attempting to open for input will fail. An empty file can be opened for output only. When you open for output, COBOL will write a dummy record to the file & then delete it out.
Q49) How do you initialize a VSAM file before any operation ? a VSAM with alternate index ?A49) Can write a dummy program that just opens the file for output and then closes it.
Q50) What does a file status of 02 on a VSAM indicate ?A50) Duplicate alternate key . Happens on both input and output operation
Q51) How do you calculate record size of an alternate cluster ? Give your values for both unique and nonunique.
A51) Unique Case: 5 + ( alt-key-length + primary-key )
Non unique Case: 5 + ( alt-key-length + n * primary-key ) where n = number of duplicate records for the alternate key
Q52) What is the difference between sequential files and ESDS files ?A52) Sequential (QSAM) files can be created on tape while ESDS files cannot. Also, you can have ALTINDEX for an ESDS while no such facility exists for QSAM files.
Q53) How do you load a VSAM data set with records ?A53) Using the REPRO command.
Q54) How do you define a GDG ?A54) Use the DEFINE GENERATIONDATAGROUP command. In the same IDCAMS step, another dataset must be defined whose DCB parameters are used when new generations of the GDG are created. This dataset is known as the model dataset. The ds name of this model dataset must be the same as that of the GDG, so use a disp of keep rather than catlg and also specify space=(trk,0)
Q55) Do all versions of the GDG have to be of the same record length ?A55) No, the DCB of the model dataset can be overridden when you allocate new versions.
Q56) How are different versions of GDG named ?A56) base-file-name.GnnnnnV00 where nnnn= generation number (upto 255). nnnn will be 0000 for the 1st generation.
Q57) Suppose 3 generations of a GDG exist. How would you reference the 1st generation in the JCL ?
A57) Use GDG name(-2).
Q58) Suppose a generation of GDG gets created in a particular step of a proc. How would you refer the current generation in a subsequent step ? What would be the disposition of this generation now ?
A58) Relative generation numbers are updated only at the end of the job, not at the end of a step. To allocate a new generation, we would be using (+1) with a DISP of (NEW,CATLG,DELETE). To refer to this in a subsequent step in the same job, we would again use (+1) but with a DISP of SHR or OLD.
Q59) What more info you should give in the DD statement while defining the next generation of a GDG ?
A59) Give (+1) as the generation number, give (new,catlg) for disp, give space parameter, can give the DCB parameter if you want to override the dcb of the model dataset.
Q60) Assuming that the DEFINE JCL is not available, how do you get info about a VSAM file's organisation ?
A60) Use the LISTCAT command.
Q61) During processing of a VSAM file, some system error occurs and it is subsequently unusable . What do you do ?
A61) Run VERIFY.
Q62) How do you fix the problem associated with VSAM out of space condition ?
A62) Define new VSAM dataset allocated with more space.
Use IDCAMS to REPRO the old VSAM file to new VSAM dataset.
Use IDCAMS to ALTER / rename the old VSAM dataset or se IDCAMS to DELETE the old VSAM dataset.
Use IDCAMS to ALTER / rename the new VSAM dataset to the name of the original VSAM dataset.
Q63) What is the meaning of VSAM RETURN-CODE 28 ?
A63) Out of space condition is raised.
Q64) On which datasets You can have ALT INDEX ?
A64) only on KSDS and ESDS - not RRDS
Q65) How many Alternate Indexes you can have on a dataset ?
A65) 255 - but you must be a nut to have so many ALT Indexes on a dataset!
Q66) Is it slower if you access a record through ALT INDEX as compared to Primary INDEX ?
A66) Yes. Why ? Because the alternate key would first locate the primary key, which in turn locates the actual record. Needs twice the number of I/Os.
Q67) What is RECOVERY and SPEED parameters in DEFINE CLUSTER command ?
A67) RECOVERY (default) and SPEED are mutually exclusive. Recovery preformats the control areas during the initial dataset load, if the job fails, you can restart but you must have a recovery routine already written to restart the job. SPEED does not preformat the CAs. It is recommended that you specify SPEED to speed up your initial data load.
Q68) Describe SHAREOPTIONS parameter (SHR) in Define Cluster command.
A68) It defines the cross-region and cross-system sharing capabilities of the dataset. Syntax is SHR(Crvalue, CSvalue) value 1 means multiple read OR single write (read integrity) 2 means multiple read AND single write (Write integrity) 3 means Multiple read AND multiple write 4 is same as 3, which refreshes the buffer with every random access. default is SHR(1 3).
Q69) What does the KEYRANGES parameter in Define Cluster commend do ?
A69) It divides a large dataset into several volumes according to the Key ranges specified. e.g., KEYRANGES ((0000001 2999999) (3000000 5999999)). if the activity on the key ranges are evenly distributed, concurrent access is possible, which is a performance improvement.
Q70) What are the optional parameters to the input dataset While loading the empty cluster with the data records ?
A70) 1)FROMADDRESS(address) 2)TOADDRESS(address) where 'address' specifies the RBA value of the key of the input record. 3)FROMNUMBER(rrn) 4)TONUMBER(rrn) where 'rrn' specifies the relative record number of the RRDS record 5)FROMKEY(key) 6)TOKEY(key) where 'key' specifies the key of the input record 7)SKIP(number) 8)COUNT(number) where 'number' specifies the number of records to skip or copy Ex: REPRO INFILE(DD1) OUTFILE(DD2) SKIP(9000) COUNT(700) - Skips the first 9000 records and begins copying at 9001 and copies 700 records from DD1 to DD2.
Q71) What is IDCAMS ? and what is the purpose of it ?
A71) IDCAMS is an access method services utility used for creating, deleting, altering VSAM files and copying sequential file to a VSAM file, etc.
Q72) How to delete a member using JCL.
A72) Using IDCAMS a member can be deleted. DELETE 'XXX.YYY(member)
Q73) What is the Difference between LDS & ESDS ?
A73) These two datasets are VSAM datasets. ESDS maintains control information. But LDS does not maintains the control information.
Q74) Is a delete operation possible in an ESDS ?B. Is rewrite operation possible in ESDS ?
A74) No delete operation is not possible in VSAM ESDS.B. Yes rewrite operation is possible in an ESDS.
Q75) What is an alternate index and path ?
A75) An alternate index is an another way of accessing key sequenced data record stored in a base cluster and path is the linkage which connect alternate index to its base cluster.
Q76) How many buffers are allotted to VSAM KSDS and ESDS ?
A76) 2 data buffers by default for ESDS. For KSDS it allots 2 data buffers and 1 index buffers. each buffer is about 4k.
Q77) what's the biggest disadvantage of using a VSAM dataset ?
A77) FREE SPACE(FPSC)
Q78) what's the device independent method to indicate where a Record is Stored ?
A78) By USING RBA(Relative Byte Address).
Q79) How many times secondary space allocated ?
A79) 122 TIMES
Q80) what is the RRN for the first record in RRDS ?
A80) The answer is : 1
Q81) what is a Base Cluster ?
A81) The Index and data components of a KSDS
Q82) If FSPC(100 100) is specified does it mean that both the control interval and control area will be left empty because 100 % of both CI and ca are specified to be empty ?
A82) No, they would not be left empty. one record will be written in each CI and 1 CI will be written for each ca.
Q. What are the Environment Division considerations for random processing of KSDS File? |
When you want to do random processing of the records in a KSDS File, the COBOL SELECT statement has the following syntax :
SELECT filename
ASSIGN TO ddname
ORGANIZATION IS INDEXED
ACCESS MODE IS RANDOM
RECORD KEY IS name-of-key-field-in-record
FILE STATUS IS file-status-area
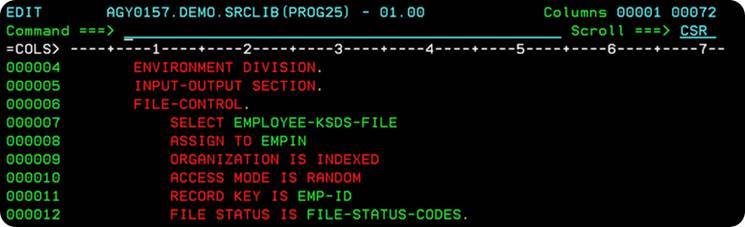
The Key field that is used to uniquely identify each employee is the Employee Identification no. – EMP-ID field. |
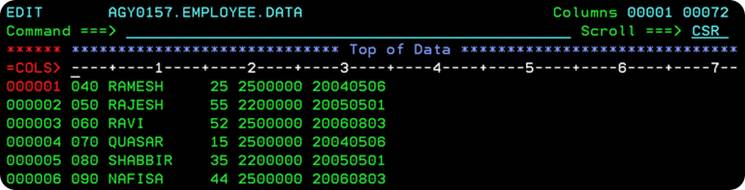
Q. How Random retrieval of KSDS Files works? |
For the sake of example, let’s assume that we have a KSDS File containing Employee records. The contents of the KSDS file are -
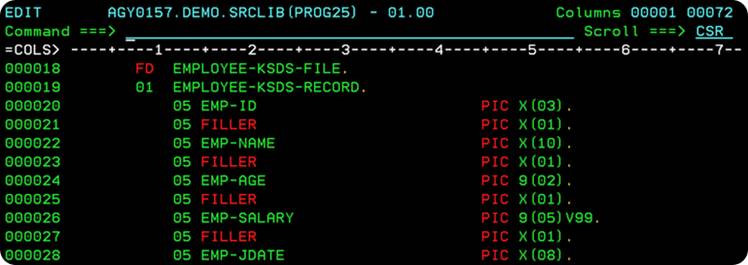
The record-layout for the Employees KSDS file is as shown below -
For random retrieval of records, you just spell out the key-value(Employee identification no.) of the employee you wanna find, to VSAM and in a jiffy, VSAM fetches the Employee details for you. Now, let’s look at what happens in the background.
The key value(employee-id) of the Employee record, you want to fetch is first placed in the key-field area(EMP-ID). Let’s assume you want to retrieve the details – name, age, salary and joining date of the Employee No. 70.
VSAM compares the RECORD KEY value(Employee-id) specified in the program, to the entries in the root index set record. The first entry in the root index record >= RECORD KEY value, is used to point to the next lower level index set record. The entries in this index record is then compared to the RECORD KEY. Again the first entry >= RECORD KEY value is found, and points to a next lower level index set record.
This search process continues downward through the index levels, until an index entry points to a sequence set record. The first sequence set entry which is greater than or equal to the (RECORD KEY)Employee No. 70, points to the Control Interval(CI) in the KSDS Data file. This Control Interval(CI) must hold the record(if it is in the file). The CI is now retrieved and searched for the desired logical record. |
Q. What are the PROCEDURE DIVISION statements for random retrieval of records in KSDS file. |
You are going to write a COBOL Program to search the details of Employee No. 70 in the Employee KSDS File. The COBOL Program can be broken down into three paragraphs – open, fetch, close.
The 1000-MAIN-PARA performs 3 steps -
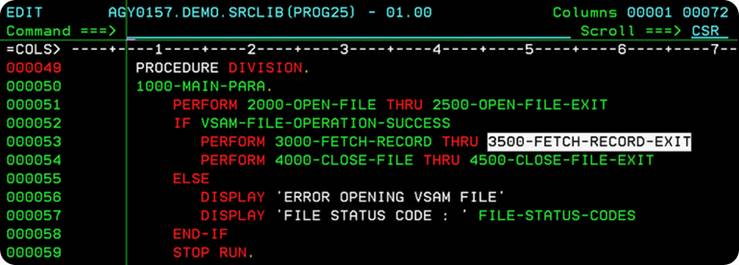
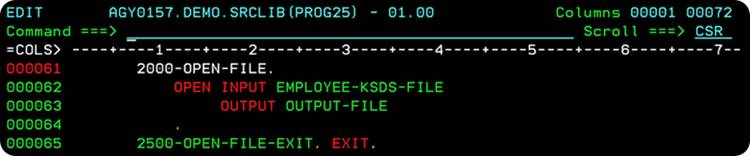
Line 51 performs 2000-OPEN-FILE-PARA, which would open the KSDS File for reading the records.
Lines 52-55 are executed, only if the Open operation on the KSDS File is successful. If the Open operation fails, a message stating ERROR OPENING VSAM FILE is displayed, and the error code is printed to the log.
If the OPEN operation is successful, you go ahead and fetch the logical-record you want, and then close the files, once you are done.
The 2000-OPEN-FILE paragraph OPENs the EMPLOYEE-KSDS-FILE containing Employee records in INPUT mode. The INPUT mode is used to read the records from a file. It also OPENs the OUTPUT-FILE in OUTPUT mode. The OUTPUT-FILE points to the log(print output) of the job, and we shall print the details of the Employee we want, to the OUTPUT-FILE.
The 3000-FETCH-RECORD paragraph will retrieve(search) the details of Employee-ID 70.
We begin by placing the key value(employee-id) of the employee, we would like to search in the RECORD KEY field – EMP-ID. Lines 68 places the value '070' in the Key-field EMP-ID.
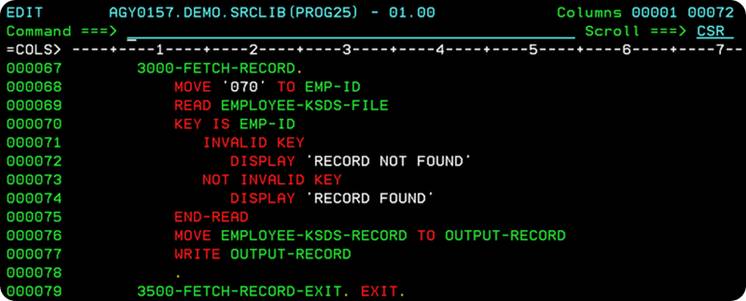
On Line 69, the COBOL READ Statement, causes VSAM to perform a random search on the EMPLOYEE-KSDS-FILE for the record with EMP-ID 70. If the search returns positive results - Employee record with EMP-ID=70 is found, the
NOT INVALID KEY clause is executed, and a message ‘RECORD FOUND’ is printed to the log. If the search is a failure – there is no Employee record in the KSDS File with EMP-ID=70, the INVALID KEY clause is executed, and a message ‘RECORD NOT FOUND’ is printed to the log.
We then store the data present in the EMPLOYEE-KSDS-RECORD area into
OUTPUT-RECORD area. Line 77 write the OUTPUT-RECORD, details of the Employee no. 70 to the OUTPUT-FILE.
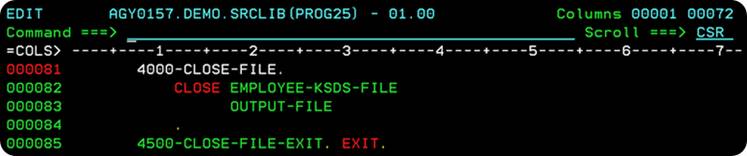
The 4000-CLOSE-PARA closes the files, and releases them.
 |